 Digestive enzymes are natural substances produced by the body to help break down food molecules into smaller particles that can be easily absorbed and used by the body. These enzymes are essential for the proper digestion and absorption of nutrients from food. They are produced by various organs in the body, including the pancreas, stomach, and small intestine, and include enzymes such as proteases, lipases, amylases, and lactases.
Digestive enzymes are natural substances produced by the body to help break down food molecules into smaller particles that can be easily absorbed and used by the body. These enzymes are essential for the proper digestion and absorption of nutrients from food. They are produced by various organs in the body, including the pancreas, stomach, and small intestine, and include enzymes such as proteases, lipases, amylases, and lactases.
In addition to being produced by the body, digestive enzymes are also available as dietary supplements. These supplements are used to support digestion and alleviate digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas, and indigestion. They are often used by people with conditions that affect the digestive system, such as pancreatic insufficiency, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Digestive enzyme supplements come in various forms, including capsules, tablets, powders, and liquids. They may be derived from animal or plant sources, and are often formulated to target specific types of food or specific digestive issues.
Overall, digestive enzymes play a critical role in the digestive process and are essential for maintaining optimal digestive health. While they are naturally produced by the body, supplements can be used to support digestive function and alleviate digestive symptoms.
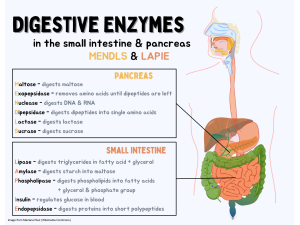
The four main digestive enzymes are:
- Proteases: These enzymes break down proteins into smaller amino acids. Examples of proteases include pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin.
- Lipases: These enzymes break down fats or lipids into smaller fatty acids and glycerol. Examples of lipases include pancreatic lipase and gastric lipase.
- Amylases: These enzymes break down carbohydrates, such as starch and glycogen, into smaller sugar molecules. Examples of amylases include salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase.
- Nucleases: These enzymes break down nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, into nucleotides. Examples of nucleases include deoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease.
These digestive enzymes are produced by different organs in the digestive system. For example, proteases are produced in the stomach and small intestine, while lipases are produced in the pancreas and small intestine. Amylases are produced in the salivary glands, pancreas, and small intestine, while nucleases are produced in the pancreas and small intestine. Together, these enzymes work to break down the different components of food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the body.
Digestive enzymes are essential for the proper digestion and absorption of nutrients from food. The body naturally produces these enzymes, but they can also be obtained from food and dietary supplements. For people with certain digestive disorders, such as pancreatic insufficiency or celiac disease, taking digestive enzyme supplements may be helpful in improving digestion and alleviating symptoms.
In addition, some research suggests that digestive enzyme supplements may be beneficial for people with conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), as well as for older adults who may have reduced enzyme production.
However, it’s important to note that not everyone needs to take digestive enzyme supplements, and they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. In addition, some people may experience side effects from these supplements, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea.
Overall, digestive enzymes are important for optimal digestive health, and can be beneficial for people with certain digestive disorders or conditions. However, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional before taking digestive enzyme supplements to determine if they are right for you.
The strength of a digestive enzyme depends on its specific function in the digestive process. Different enzymes are responsible for breaking down different types of food molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
In terms of protein digestion, the strongest digestive enzyme is believed to be pepsin, which is produced by the stomach. Pepsin is highly effective at breaking down proteins into smaller peptides, which can then be further broken down by other proteases in the small intestine.
For fat digestion, the strongest digestive enzyme is pancreatic lipase, which is produced by the pancreas and secreted into the small intestine. Pancreatic lipase is highly effective at breaking down fats into smaller fatty acids and glycerol, which can be absorbed by the body.
For carbohydrate digestion, the strongest digestive enzyme is amylase, which is produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. Amylase is highly effective at breaking down complex carbohydrates, such as starch, into smaller glucose molecules, which can be absorbed by the body.
Overall, each digestive enzyme plays a critical role in the digestive process, and the strength of each enzyme depends on its specific function in breaking down different types of food molecules.
The main producer of digestive enzymes is the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen that produces several digestive enzymes, including proteases, lipases, and amylases. These enzymes are secreted into the small intestine, where they help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
In addition to the pancreas, other organs in the digestive system also produce digestive enzymes. For example, the salivary glands produce amylase, which starts the digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth. The stomach produces proteases, such as pepsin, which break down proteins. The small intestine also produces enzymes, including lactase, sucrase, and maltase, which help break down different types of sugars.
Together, these digestive enzymes work to break down the different components of food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body, and the pancreas plays a crucial role in this process by producing several of the key enzymes needed for proper digestion and nutrient absorption.

