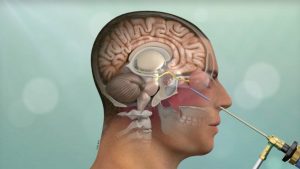
Neuroendoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used in the treatment of various conditions of the brain and spinal cord. The procedure involves the use of an endoscope, which is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to it, to visualize and access the interior of the brain or spinal cord.
Neuroendoscopy is performed to diagnose and treat a range of conditions, including brain tumors, hydrocephalus, intracranial hematomas, and spinal cord lesions. The main benefits of neuroendoscopy compared to traditional open brain or spinal surgery include reduced trauma to the patient, less pain and faster recovery, and improved outcomes.
Neuroendoscopy is performed by trained neurosurgeons and is typically performed under general anesthesia. The procedure is performed through small incisions in the skull or spinal column, and the endoscope is used to visualize the interior of the brain or spinal cord and perform the necessary procedures.
Overall, neuroendoscopy is a safe and effective procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of brain and spinal cord conditions, offering patients a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery.
Get Sample PDF Report with Graphs and Figures Here
Neuroendoscopy is used for the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord. Some of the common applications of neuroendoscopy include:
- Brain tumors: Neuroendoscopy can be used to remove small to medium-sized brain tumors through small incisions, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue.
- Hydrocephalus: Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Neuroendoscopy can be used to relieve this buildup of fluid by creating a shunt or by removing the obstruction that is causing the fluid buildup.
- Intracranial hematomas: Neuroendoscopy can be used to remove blood clots and other types of hematomas that form in the brain after a traumatic injury.
- Spinal cord lesions: Neuroendoscopy can be used to access and remove lesions or tumors located within the spinal cord.
- Diagnosis and treatment of other intracranial conditions: Neuroendoscopy can also be used to diagnose and treat other conditions of the brain and spinal cord, such as cysts, abscesses, and other lesions.
Overall, neuroendoscopy offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open brain or spinal surgery, providing a safe and effective way to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord.
What is the recovery for Neuroendoscopy?
The recovery time for neuroendoscopy can vary depending on the specific procedure and the overall health of the patient. However, in general, neuroendoscopy is considered to be a minimally invasive procedure that is associated with a faster recovery time compared to traditional open brain or spinal surgery.
After the procedure, patients are usually observed in the hospital for several days to ensure that they are recovering properly. They may experience some discomfort, such as headaches or neck pain, which can usually be managed with medication.
Most patients are able to return to their normal activities within a few days to a few weeks after the procedure. However, it is important to follow the specific instructions provided by the treating physician regarding post-operative care and recovery, including any restrictions on physical activity.
In some cases, additional rehabilitation or therapy may be necessary, depending on the specific condition being treated and the extent of the procedure.
It is also important for patients to attend all follow-up appointments with their treating physician to monitor their progress and ensure that they are recovering well.
A neuroendoscopy procedure typically requires a number of different instruments and equipment, including:
- Endoscope: This is a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it, which is used to visualize and access the interior of the brain or spinal cord.
- Guide tube: A guide tube is a metal or plastic tube that is inserted into the brain or spinal cord to provide a pathway for the endoscope to reach the target area.
- Suction and irrigation devices: These devices are used to remove fluid and debris during the procedure.
- Scissors and forceps: Scissors and forceps are used to remove tissue, such as tumors or other masses, during the procedure.
- Biopsy instruments: Biopsy instruments, such as needles or probes, may be used to obtain tissue samples for diagnostic purposes.
- Microdissectors: Microdissectors are specialized tools that are used to separate and remove tissue during the procedure.
- Stents and shunts: Stents and shunts may be placed to relieve fluid buildup or to support the structure of the brain or spinal cord.
- Monitoring equipment: Monitoring equipment, such as electroencephalography (EEG) or cerebral oximetry monitors, may be used to monitor the patient’s brain activity and vital signs during the procedure.
The specific instruments used during a neuroendoscopy procedure will depend on the specific condition being treated and the needs of the patient. The treating neurosurgeon will work with a team of healthcare professionals to ensure that the appropriate instruments and equipment are available and ready for use during the procedure.
Some of the common risks associated with neurosurgery include:
- Infection: There is always a risk of infection when undergoing any type of surgery, including neurosurgery. This risk can be reduced by following proper infection control procedures.
- Bleeding: Neurosurgery involves accessing the brain or spinal cord, which are both surrounded by blood vessels. There is a risk of bleeding during the procedure, which can lead to increased pressure within the skull or spinal canal.
- Nerve damage: Neurosurgery can sometimes result in damage to the nerves that control sensation, movement, or other functions.
- Stroke: There is a risk of stroke during neurosurgery, particularly if the procedure involves the blood vessels within the brain.
- Cognitive and motor deficits: Neurosurgery can sometimes result in cognitive or motor deficits, such as memory loss, difficulty speaking, or loss of dexterity.
- Anesthesia complications: Like any surgery, neurosurgery involves the use of anesthesia, which can carry its own risks, such as breathing difficulties or allergic reactions.
However, it is important to keep in mind that neurosurgery is often performed to treat conditions that can be life-threatening or significantly impair quality of life, and the benefits of the procedure can outweigh the risks in many cases.
It is always important to discuss the specific risks and benefits of neurosurgery with a qualified neurosurgeon before undergoing the procedure.
Contact:
David Correa
USA/Canada (Toll-Free): +1-800-792-5285, +1-503-894-6022
Fax: +1(855)550-5975
help@alliedmarketresearch.com