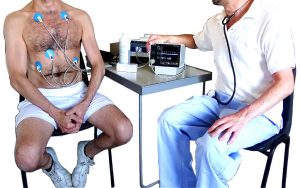
Medical electrodes are devices that are used to detect and record electrical signals from the body. They are commonly used in medical procedures such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG).
Medical electrodes are typically made of a conductive material, such as metal or carbon, that can pick up electrical signals from the body. They are attached to the skin using an adhesive, and can be designed in a variety of shapes and sizes to fit different areas of the body. The global medical electrodes market size was valued at $1.7 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $2.4 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 3.6% from 2022 to 2031.
The electrical signals picked up by the electrodes are transmitted through wires to a recording device, which processes and displays the information in a way that can be interpreted by a healthcare provider. This information can be used to diagnose a variety of medical conditions, such as heart rhythm abnormalities, seizures, and muscle disorders. Overall, medical electrodes are an important tool in modern medicine, allowing for the accurate detection and diagnosis of a wide range of medical conditions.
What electrodes are used in medical devices?
There are several types of electrodes that are commonly used in medical devices, depending on the specific application. Here are a few examples:
- Surface electrodes: These are electrodes that are placed directly on the surface of the skin to detect electrical activity, such as in electrocardiography (ECG), electromyography (EMG), and electroencephalography (EEG).
- Needle electrodes: These are thin, needle-like electrodes that are inserted into the muscle tissue to detect electrical activity, such as in electromyography (EMG).
- Fetal scalp electrodes: These are small electrodes that are attached to the baby’s scalp during labor to monitor the baby’s heart rate and detect signs of distress.
- Intraoperative electrodes: These are electrodes that are used during surgical procedures to monitor the function of nerves and muscles, and to help guide the surgeon’s actions.
- Cardiac ablation electrodes: These are specialized electrodes that are used in cardiac ablation procedures to deliver energy to the heart tissue and create scar tissue to treat certain heart conditions.
These are just a few examples of the many types of electrodes that are used in medical devices. The specific type of electrode used will depend on the intended use of the device and the specific medical condition being treated or monitored.
Download Free Sample PDF:
https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-sample/2074
What are electrodes medical uses?
Electrodes have several medical uses, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes for monitoring heart activity
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) electrodes for measuring brain activity
- Electromyogram (EMG) electrodes for assessing muscle function
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) electrodes for pain relief
- Defibrillator electrodes for delivering an electric shock to restart the heart
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) electrodes for treating severe depression or other mental illnesses
- Electrosurgical electrodes for cutting or coagulating tissue during surgical procedures.
How medical electrodes are made?
Medical electrodes are typically made by using a combination of conductive materials and adhesives. The exact materials used may vary depending on the type of electrode being made and the specific application it will be used for.
The basic steps involved in making a medical electrode are:
- Choosing the conductive material: The material used for the electrode must be able to conduct electrical signals effectively. Common materials used include silver, silver chloride, carbon, and stainless steel.
- Applying the conductive material: The conductive material is applied to a substrate, which is typically a flexible backing material. This can be done by printing, coating, or laminating the conductive material onto the substrate.
- Applying the adhesive: An adhesive layer is applied on top of the conductive material, to adhere the electrode to the patient’s skin.
- Cutting the electrodes: The electrodes are cut into the desired size and shape, typically circular or rectangular.
- Packaging the electrodes: The electrodes are packaged to keep them sterile until they are ready to be used.
Quality control and testing are important steps throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the electrodes are safe and effective for medical use.
Contact:
David Correa
USA/Canada (Toll Free): +1-800-792-5285, +1-503-894-6022

